What is Cost Accounting? [With PDF]
Cost accounting is an essential tool that helps businesses understand their financial health, streamline operations, and maximize profits.
In today’s competitive business environment, cost accounting plays a pivotal role in decision-making by providing detailed insights into costs associated with production, operations, and services.
But what exactly is cost accounting, and why is it important? Let’s dive deeper to unravel the fundamentals.
Why is Understanding Cost Accounting Important?
Imagine you’re running a bakery. You bake cakes, cookies, and bread, but do you know how much it costs to make each item? Are you pricing your products correctly to cover costs and make a profit?
Cost accounting answers these questions, helping businesses of all sizes make informed decisions about pricing, budgeting, and strategy. Without it, you could be losing money without even realizing it.
What is Cost Accounting?
Cost accounting is the process of recording, analyzing, and reporting all costs involved in producing goods or providing services.
Unlike financial accounting, which focuses on a company’s overall financial performance, cost accounting zeroes in on internal processes. This method helps businesses identify areas where they can reduce costs, increase efficiency, and improve profitability.
Primary Goals of Cost Accounting:
- Determine Costs: Calculate the total cost of production or service.
- Control Costs: Identify and eliminate unnecessary expenses.
- Aid Decision-Making: Provide data for strategic planning, such as pricing or expansion decisions.
- Improve Efficiency: Optimize resource allocation.
Key Components of Cost Accounting
1. Cost Types
Understanding the types of costs is critical for effective cost accounting:
- Direct Costs: Costs directly tied to production, such as raw materials and labor.
- Indirect Costs: Overhead expenses like rent, utilities, and administrative salaries.
- Fixed Costs: Costs that remain constant regardless of production levels, like lease payments.
- Variable Costs: Costs that change with production volume, such as raw materials.
2. Cost Allocation
Cost allocation involves distributing costs to different departments or products. For example, if your bakery uses 50% of its electricity for baking and 50% for packaging, you allocate the electricity bill accordingly.
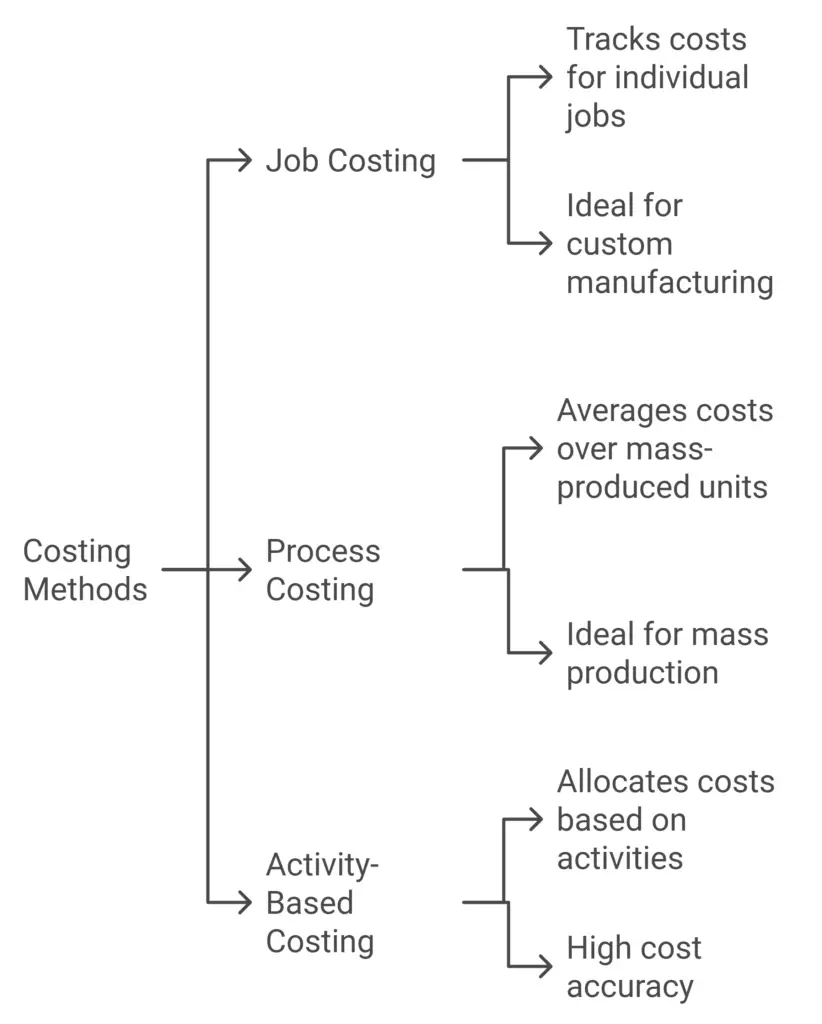
3. Costing Methods
- Job Costing: Assigns costs to specific jobs or projects, ideal for custom orders.
- Process Costing: Tracks costs by process, suitable for mass production industries.
- Activity-Based Costing (ABC): Allocates costs based on activities that drive expenses, offering more precision.
Practical Example: Cost Accounting in Action
Let’s revisit the bakery example. Suppose you want to price a chocolate cake:
- Direct Costs: Ingredients like flour, cocoa, and sugar cost $5 per cake.
- Indirect Costs: Utilities and equipment maintenance add $2 per cake.
- Fixed Costs: Rent and insurance amount to $1 per cake when spread across all items.
- Variable Costs: Packaging adds $0.50 per cake.
By adding all these costs, you determine the total cost of producing one cake is $8.50. With this insight, you can set a profitable selling price above this amount.
Benefits of Cost Accounting
- Accurate Pricing: Ensures products and services are priced to cover costs and generate profit.
- Cost Control: Highlights inefficiencies and areas for cost reduction.
- Budgeting: Aids in creating realistic budgets based on detailed cost data.
- Profitability Analysis: Identifies which products or services are most profitable.
- Improved Decision-Making: Empowers businesses to make informed strategic decisions.
Test Your Knowledge: Quick Quiz
Challenges in Cost Accounting
While cost accounting is invaluable, it comes with challenges:
- Complexity: Gathering and analyzing data can be time-consuming.
- Accuracy: Errors in data collection or allocation can skew results.
- Cost: Implementing sophisticated cost accounting systems can be expensive.
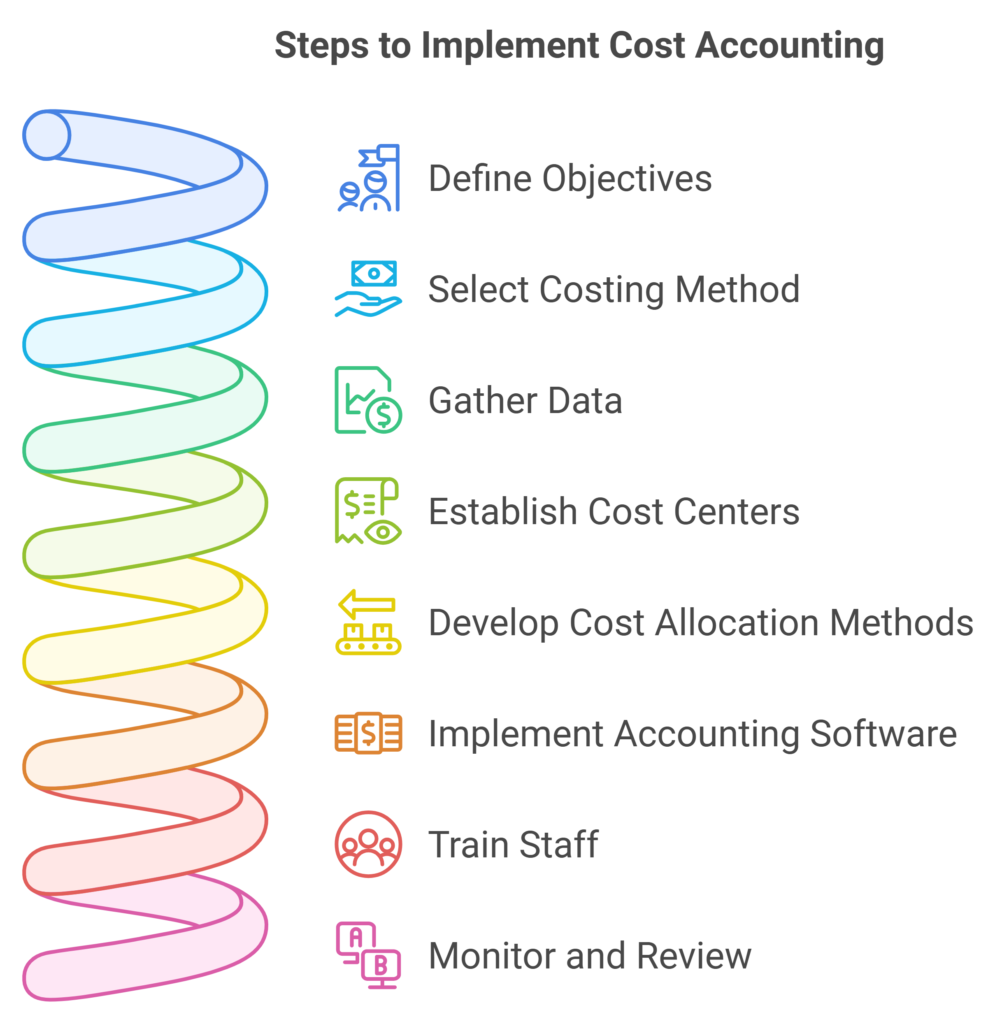
Overcoming Challenges
- Invest in reliable accounting software.
- Train staff to understand and implement cost accounting principles.
- Regularly review and update costing methods.
Key Takeaways
- Cost accounting is essential for understanding and managing business costs.
- It helps in pricing, budgeting, and improving profitability.
- Different costing methods suit different business needs.
- Overcoming challenges requires proper tools, training, and regular review.</ol>
Call-to-Action
Want to dive deeper into cost accounting? Explore our cost accounting tutorials, download our free cost allocation template, or test your skills with our interactive cost accounting quizzes.
By mastering cost accounting, you’re taking a significant step towards better financial control and business success. Start today!







